Mastering Graphs for GCSE Maths: A Complete Guide to Exam Success
Mastering graphs for GCSE Maths is an essential part of GCSE math, providing a visual way to represent mathematical relationships. Whether you’re plotting linear equations, quadratic curves, or interpreting statistical graphs, mastering graphs is a crucial skill for exam success.
In this guide, we’ll cover the different types of graphs, key techniques for plotting them, and expert tips to help you improve your understanding of graphs in GCSE Maths.
Why Mastering Graphs for GCSE Maths is Important
Understanding graphs is vital because:
- They Visually Represent Data – Graphs help illustrate relationships between variables in a way that’s easier to interpret.
- They Have Real-World Applications – Graphs are widely used in science, business, and economics for data analysis and trend predictions.
- They Are Key to Exam Success – Graph-related questions frequently appear in GCSE Maths exams, often as problem-solving tasks.
Types of Graphs in GCSE Maths
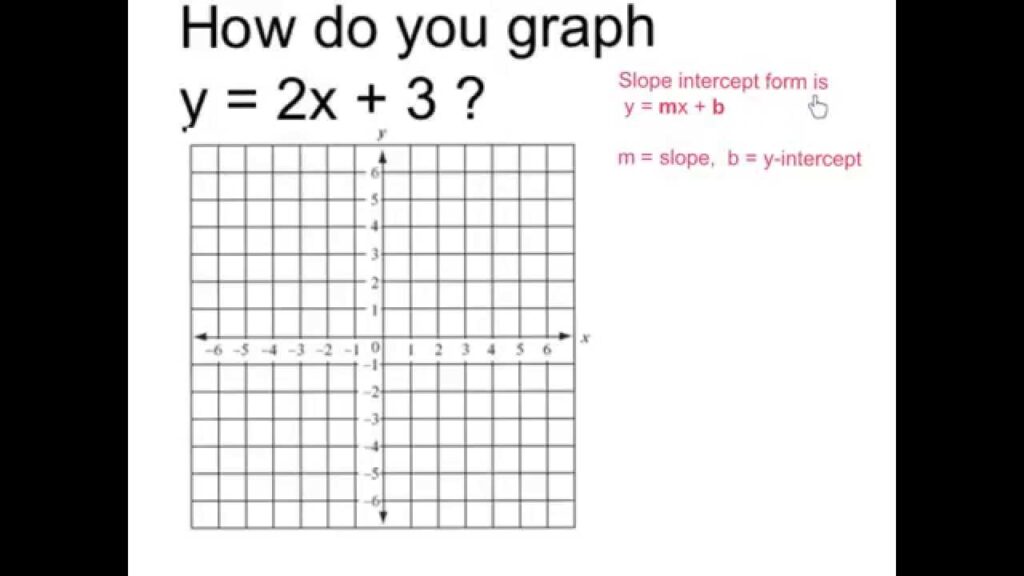
1. Linear Graphs
Linear graphs represent straight-line relationships and follow the equation:
y=mx+c
Where:
- m is the slope (gradient).
- c is the y-intercept (where the line crosses the y-axis).
Example:
Plot the graph of y = 2x + 1:
- When x = 0, y = 1.
- When x = 1, y = 3.
✅ Action Step: Practice plotting different linear graphs and identifying gradients and intercepts.
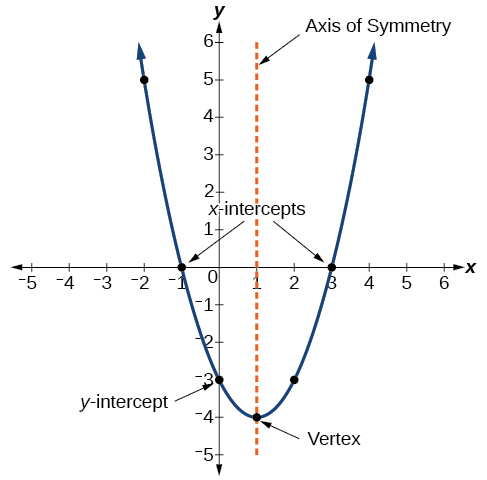
2. Quadratic Graphs
Quadratic graphs create parabolas and follow the equation:
y=ax^2 + bx + c
- If a > 0, the parabola opens upward.
- If a < 0, the parabola opens downward.
Example:
Plot y = x^2 – 4x + 3 by:
- Finding the vertex, roots, and y-intercept.
- Plotting key points and connecting them smoothly.
✅ Action Step: Practice sketching quadratic graphs and identifying turning points.
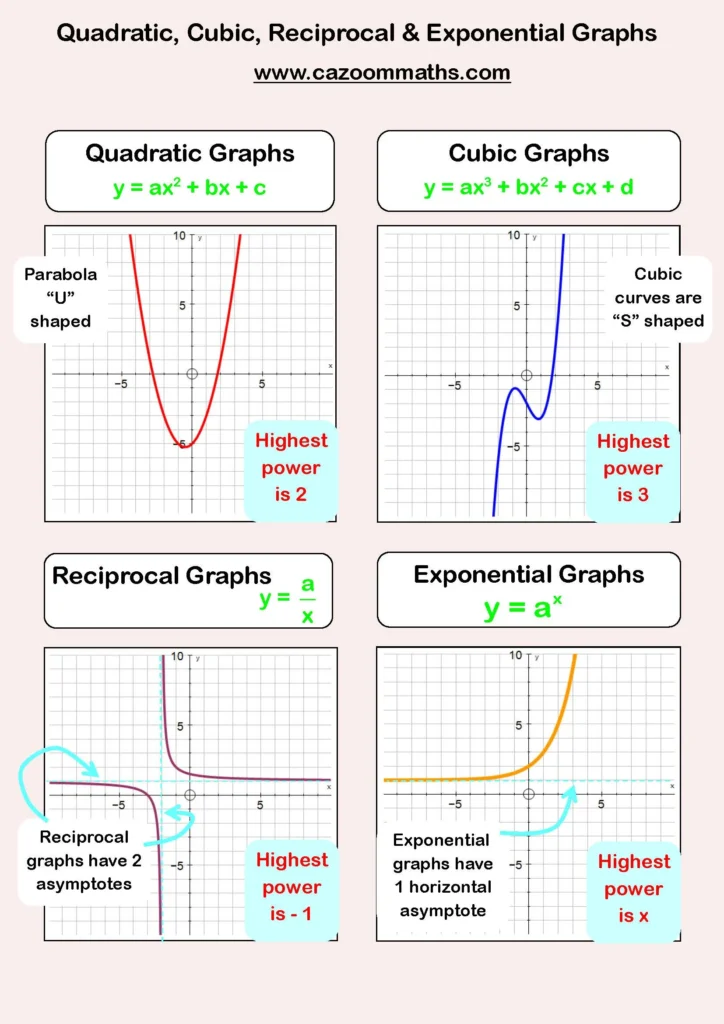
3. Cubic Graphs
Cubic graphs follow the equation:
y = a/x
- These graphs have two separate branches and approach asymptotes (lines the graph gets close to but never touches).
Example:
Plot y = 2/x and observe how the graph:
- Avoids touching the x-axis and y-axis.
- Forms two separate curves in different quadrants.
✅ Action Step: Study the properties of reciprocal graphs and how asymptotes affect their shape.
4. Reciprocal Graphs
Exponential graphs follow the equation:
y=a^x
- These graphs have two separate branches and approach asymptotes (lines the graph gets close to but never touches).
Example:
Plot y = 2/x and observe how the graph:
- Avoids touching the x-axis and y-axis.
- Forms two separate curves in different quadrants.
✅ Action Step: Study the properties of reciprocal graphs and how asymptotes affect their shape.

5. Exponential Graphs
Exponential graphs follow the equation:
y=a^x
- If a > 1, the graph shows exponential growth.
- If 0 < a < 1, the graph shows exponential decay.
Example:
Plot y = 2^x, noting that:
- The graph starts small but grows rapidly as x increases.
- The y-axis is an asymptote, meaning the graph never reaches zero.
✅ Action Step: Practice plotting and analyzing exponential functions.
6. Solve for Missing Angles Using Inverse Trigonometry
To find a missing angle, use inverse trigonometric functions:
Example:
If opposite = 5 cm and hypotenuse = 10 cm, find θ\thetaθ:
sin(θ)=510=0.5\sin(\theta) = \frac{5}{10} = 0.5sin(θ)=105=0.5 θ=sin−1(0.5)=30∘\theta = \sin^{-1}(0.5) = 30^\circθ=sin−1(0.5)=30∘
📌 Action Step:
✔ Practice using sin⁻¹, cos⁻¹, and tan⁻¹ to find missing angles.
Key Skills for Mastering Graphs for GCSE Maths
1. Accurate Plotting
- Always use a ruler and evenly spaced scales when plotting points.
- Label axes clearly and check coordinates carefully.
✅ Action Step: Practice plotting various equations on graph paper.
2. Identifying Key Features
Recognizing important graph features helps solve questions faster. These include:
- Intercepts – Where the graph crosses the x-axis and y-axis.
- Turning Points – The highest or lowest point of the graph.
- Asymptotes – Lines that the graph approaches but never touches.
✅ Action Step: Identify these features in different graph types.
3. Interpreting Graphs
Graphs are often used to represent real-world data. Example applications include:
- Distance-time graphs for speed calculations.
- Population growth graphs for trend analysis.
✅ Action Step: Practice interpreting and extracting information from different types of graphs.
4. Solving Equations Graphically
Graphs can help solve equations by finding points of intersection.
Example:
Solve x^2 – 4x + 3 = 0 by:
- Plotting y = x^2 – 4x + 3.
- Finding the x-values where y = 0.
✅ Action Step: Practice solving quadratic, linear, and simultaneous equations using graphs.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Incorrect Plotting: Always double-check your coordinates.
- Misinterpreting Features: Ensure you understand what intercepts, turning points, and asymptotes mean.
- Ignoring Scales and Units: Check the units when analyzing real-world graphs.
How a GCSE Maths Tutor Can Help
A GCSE Maths tutor can provide personalized guidance to improve your graphing skills, helping you:
- Understand difficult graph topics in depth.
- Solve past paper questions effectively.
- Gain confidence in using graphs for problem-solving.
✅ Action Step: Visit MathZem to find an experienced tutor to help you with Mastering Graphs for GCSE Maths.
FAQs About Mastering Graphs for GCSE Maths
1. What’s the best way to memorize graph equations?
Use flashcards, write equations down repeatedly, and apply them in practice questions.
2. How do I solve problems involving graphs?
Identify the type of graph, plot it accurately, and analyze key features like intercepts and gradients.
3. Can I use a calculator for graphing?
Yes, but it’s important to understand how graphs behave without relying on technology.
4. What if I’m stuck on a graph problem?
Break it down into smaller steps, check your calculations, and seek help from a tutor.
Final Thoughts
Mastering Graphs for GCSE Maths is crucial for exam success. By understanding different graph types, practicing regularly, and using the right strategies, you can confidently tackle any graph-related question.
✅ Action Step: Start practicing today and explore expert resources at MathZem to boost your GCSE math skills!






